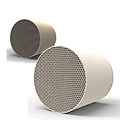
Catalyst Materials 1. Substrate: Cordierite (low thermal expansion, strong thermal shock resistance). Gasoline engine TWC honeycomb matrix: Silicon carbide (SiC). High thermal conductivity, high strength. High-temperature diesel catalyst/industrial exhaust gas. The substrate structure typically features honeycomb or sheet-like corrugated channels to reduce backpressure and provide a large surface area.
2. Washcoat • Primarily composed of γ-Al₂O₃, CeO₂-ZrO₂, and TiO₂ • Functions: • Increases specific surface area (providing hundreds of square meters/g) • Immobilizes precious metals • Provides oxygen storage and release capabilities • Typically 10–30 μm thick, with a microporous structure ensuring adequate contact between gas and metal
3. Precious Metal Catalytic Layer • Platinum (Pt): Oxidizes CO and HC • Palladium (Pd): Oxidizes HC and CO • Rhodium (Rh): Reduces NOₓ Precious metals are formed into nanoparticles through impregnation, drying, and calcination, and then dispersed within the pores of the washcoat, ensuring high activity and durability.