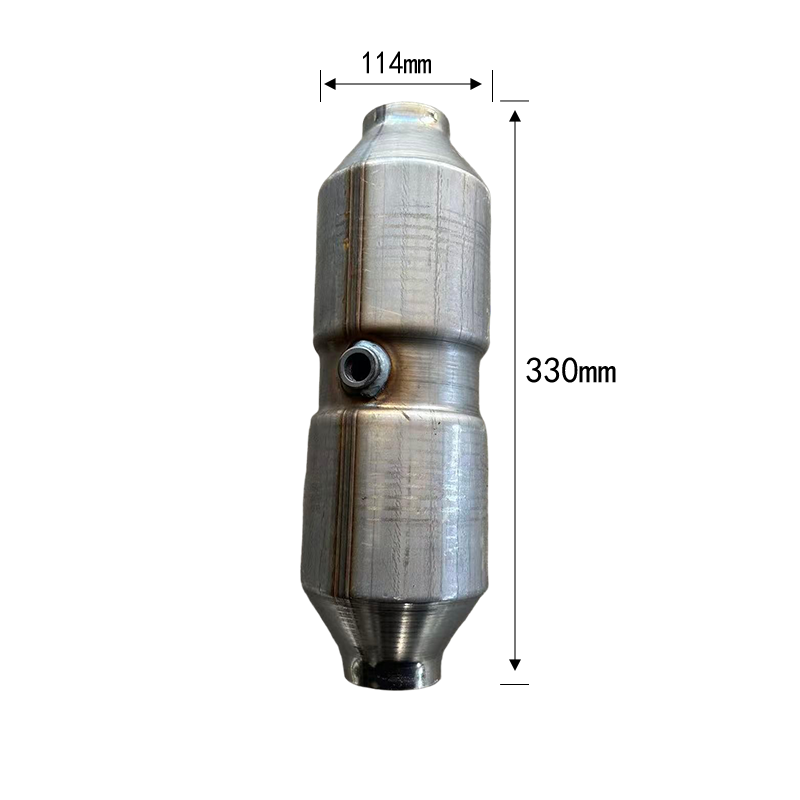
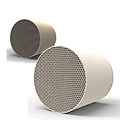
Working Principle 1. Working Mechanism of a Three-Way Catalytic Converter The core goal of a three-way catalytic converter is to simultaneously complete oxidation and reduction reactions: 1. CO oxidation reaction: CO + ½O₂ → CO₂ 2. HC oxidation reaction: CxHy + (x + y/4) O₂ → xCO₂ + y/2 H₂ O 3. NOₓ reduction reaction: 2NO → N₂ + O₂ or 2NO + 2CO → N₂ + 2CO₂ As gas flows through the honeycomb substrate inside the catalyst, the precious metal particles adsorb gas molecules and reduce the activation energy, enabling the reaction to proceed efficiently at low temperatures. Temperature control is crucial, with optimal conversion rates typically achieved between 200–800°C.
Oxygen Storage-Release Mechanism (OSC): To address fluctuations in the air/fuel ratio during different engine combustion conditions, the TWC utilizes a CeO₂–ZrO₂ oxygen storage system: • During oxygen-rich conditions, excess oxygen is stored. • During oxygen-lean conditions, the stored oxygen is released to ensure smooth CO/HC oxidation and NOₓ reduction reactions.