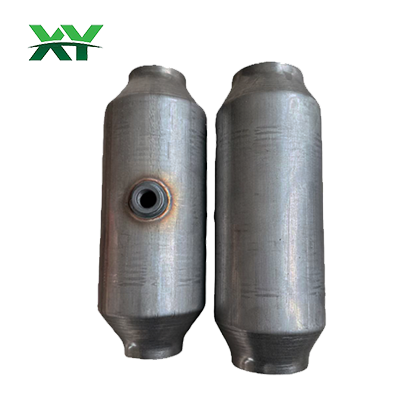
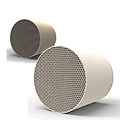
I. Overview: The catalytic converter is a key device for controlling vehicle exhaust emissions, used to reduce harmful substances in exhaust gas, such as: • Carbon monoxide (CO) • Unburned hydrocarbons (HC) • Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ). The three-way catalytic converter (TWC) is a common type of converter used in gasoline vehicles. It can simultaneously oxidize CO/HC and reduce NOₓ, hence the name "three-way." The core of a catalytic converter consists of three components: 1. Substrate: Support structure and airflow channels 2. Washcoat: Provides high surface area and metal adsorption sites 3. Precious metal catalyst layer: Active components such as Pt, Pd, and Rh
II. Working Principle 1. Working Mechanism of a Three-Way Catalytic Converter The core goal of a three-way catalytic converter is to simultaneously complete oxidation and reduction reactions: 1. CO oxidation reaction: CO + ½O₂ → CO₂ 2. HC oxidation reaction: CxHy + (x + y/4) O₂ → xCO₂ + y/2 H₂ O 3. NOₓ reduction reaction: 2NO → N₂ + O₂ or 2NO + 2CO → N₂ + 2CO₂ As gas flows through the honeycomb substrate inside the catalyst, the precious metal particles adsorb gas molecules and reduce the activation energy, enabling the reaction to proceed efficiently at low temperatures. Temperature control is crucial, with optimal conversion rates typically achieved between 200–800°C.