The three main functions of a catalytic converter are:
1. Converting carbon monoxide (CO) to carbon dioxide (CO₂).
Carbon monoxide is a toxic gas, and the catalyst oxidizes it into harmless carbon dioxide.
2. Converting hydrocarbons (HC) to carbon dioxide and water (H₂O).
Incompletely burned fuel (HC) is further oxidized by the catalyst, reducing ozone pollution and smog.
3. Reducing nitrogen oxides (NOₓ) to nitrogen (N₂) and oxygen (O₂).
The catalytic converter breaks down nitrogen oxides into harmless nitrogen and oxygen through a reduction reaction.
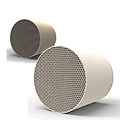
Core Components:
• Precious metal catalyst (such as platinum (Pt), palladium (Pd), rhodium (Rh))
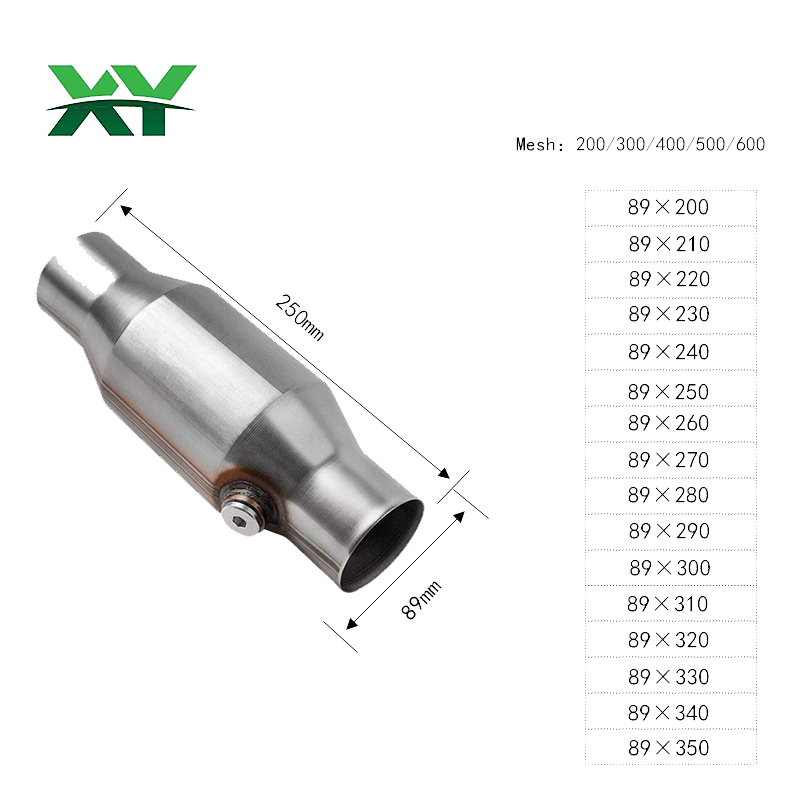
• Ceramic or metal carrier (honeycomb structure to increase contact area)
• Housing (high-temperature-resistant metal shell)
Summary:
The essential function of a catalytic converter: It converts toxic and harmful gases (CO, HC, NOₓ) in vehicle exhaust into harmless gases (CO₂, H₂O, N₂) through a chemical reaction.