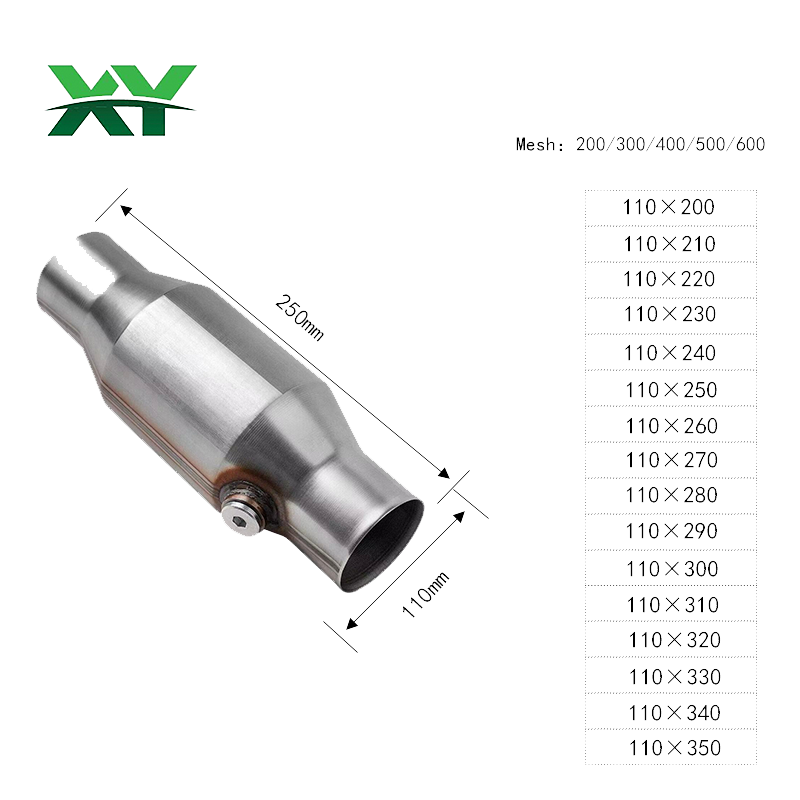
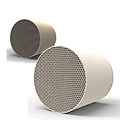
Specific uses are as follows:
1. Automotive Exhaust Treatment
• The primary application is installing catalytic converters in gasoline, diesel, and hybrid vehicles to treat harmful emissions from the engine.
• Converts:
• Carbon monoxide (CO) → to carbon dioxide (CO₂)
• Hydrocarbons (HC) → to water (H₂O) and carbon dioxide
• Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ) → to nitrogen (N₂)
2. Complying with Environmental Regulations
• Used in vehicles that meet Euro V, Euro VI, and China VI emission standards.
• A key component for passing annual vehicle inspections and obtaining environmental certification.
3. Industrial Exhaust Treatment
• Catalytic converters are also used in some factories, combustion boilers, and diesel generator sets to purify industrial exhaust gases. 4. Laboratory Gas Purification
• Small catalytic converters are also used in some laboratory equipment (such as gas chromatograph exhaust systems) to purify exhaust gases.
5. Preventing Catalyst Poisoning or Fire Risks
• Some catalytic converters also have protective functions, such as protecting the engine or other exhaust system components by controlling temperature or preventing the accumulation of toxic substances.