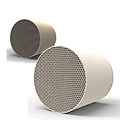
Standard Requirements:
• Precise control of precious metal content (ppm or g/L level);
• Uniform distribution to avoid local over- or under-concentration;
• Strict control of sintering temperature and time to ensure high-temperature resistance.
3. Catalytic Converter Assembly
• Secure the coated catalyst in the housing to ensure uniform airflow through the catalyst layer; • Install high-temperature, corrosion-resistant gaskets to ensure leak-free interfaces;
• Test pressure drop and exhaust gas purification efficiency to ensure compliance with customer and regulatory requirements.
III. Quality Control Standards
1. Raw Material Inspection: The carrier pore size, surface area, and chemical composition must meet design requirements;
2. Coating Uniformity Testing: Optical or X-ray inspection techniques are used to ensure uniform distribution of the precious metal;
3. High-Temperature Resistance and Thermal Cycling Testing: Ceramic and metal carriers must undergo multiple cycles of high-temperature cycling to ensure long-term stability;
4. Exhaust Gas Purification Efficiency Testing: CO, HC, and NOx conversion rates meet standard requirements;
5. Mechanical Strength and Vibration Resistance Testing: Ensure the catalyst does not break or fall off during transportation and use. ⸻
IV. Customization Advantages
• Highly Targeted: Customized design based on vehicle model, engine power, and emission standards;
• High Efficiency and Environmental Protection: Optimizing precious metal usage improves exhaust purification efficiency and reduces costs;
• High Reliability: Strict process control and testing ensure product resistance to high temperatures, vibrations, and a long lifespan;
• Traceability: Each batch of product is accompanied by production records and quality inspection reports for easy after-sales and regulatory oversight